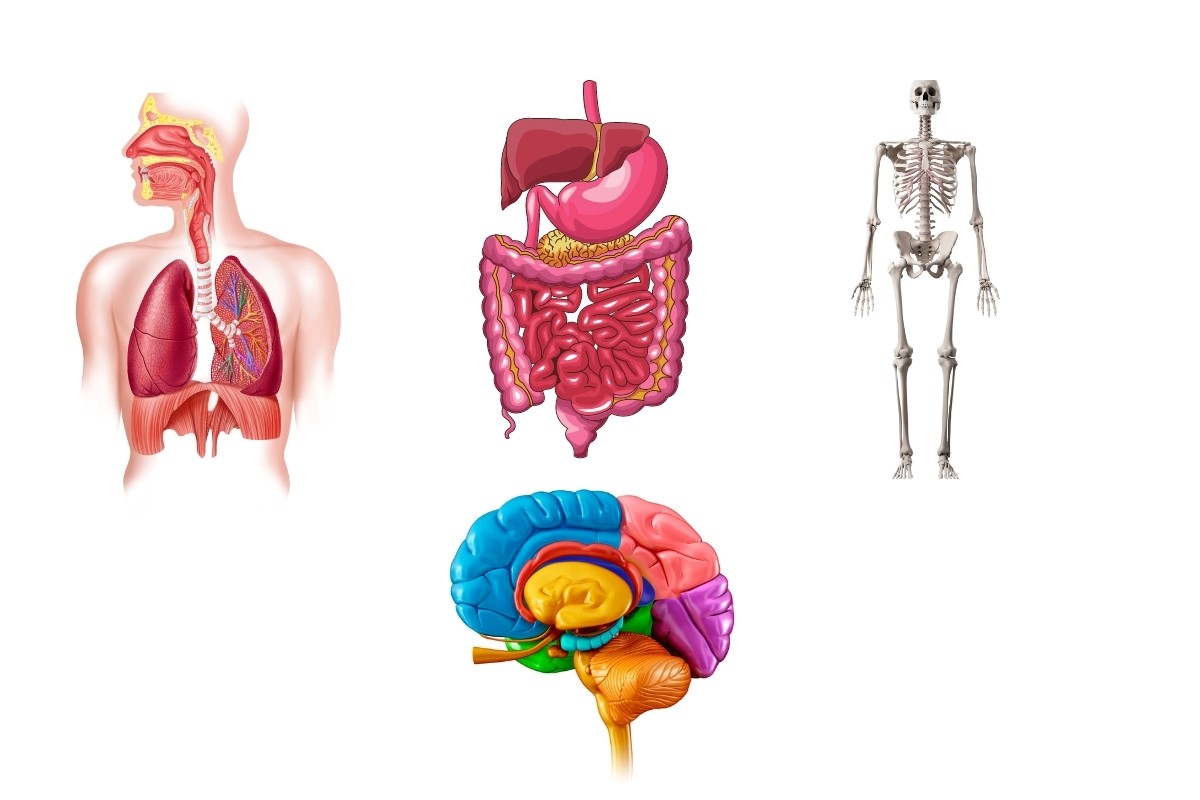
Biological Systems-Definition and Examples
Introduction
You may have heard of the term “biological system” before, but do you know what it means? A biological system is a group of organs that work together to perform a specific function.
The respiratory system takes in oxygen and releases carbon dioxide, while the digestive system breaks down food into nutrients for our bodies. There are lots of different systems in your body – take some time to learn about them!
However, should you skip this guide because of reasons such as a busy schedule, our writers are ready to ensure you do not lose anything by acing that assignment for you. Just place an order today!
Examples of Biological Systems


There are various Biological systems in the human body. They include:
The Nervous System
The nervous system is a communication highway that sends and receives signals to the brain. The body can’t function without this complex network of cells, tissues, and organs.
There are three main divisions in the Nervous System:
Central Nervous System
This system includes your brain and spinal cord. The central nervous system is the main control center for your body. It coordinates thoughts, feelings, and movement with the rest of your bodily systems.
The brain is the central nervous system’s most important part. It controls how you feel, thinks, and act by sending messages to other parts of your body.
The spinal cord is the continuation of the brain down your back, connecting to nerves in different parts of your body and carrying messages to and from the brain. This biological system is housed in your head, neck, and spine area.
Peripheral Nervous System
The peripheral system consists of the nerves that go directly to muscles and organs. It is the connection between your brain and other organs in your body. It’s made up of nerves that connect to specific parts of your body.
Nerves in the peripheral nervous system control:
- The movement of muscles and joints, such as arms swinging when you walk
- The regulation of blood pressure
- Digestion, such as when the stomach secretes acid to break down food or insulin is released for sugar
- The functioning of sweat glands and hair follicles
- Homeostasis, such as the body’s natural equilibrium for temperature regulation.
Autonomic Nervous System
This biological system is responsible for involuntary actions like breathing, heart rate, and the digestive system. The autonomic nervous system regulates the following functions:
- Heart rate and blood pressure, for example, when you’re exercising
- Digestion, such as when the stomach secretes acid to break down food or insulin is released for sugar
The Lymphatic System


The lymphatic system is another important biological system in your body. It’s made up of tubes that carry a clear fluid called lymph to filter out waste products from your blood.
This biological system is important for fighting against infection because it produces white cells to battle off bacteria or viruses that threaten your health. It is connected to the cardiovascular system and immune system because lymph comes from the interstitial fluid that filters out your blood.
The lymphatic system includes the nodes, tonsils, and thymus gland in your neck region, as well as the spleen, liver, and bone marrow.
Respiratory System
The respiratory system consists of your nose, throat, and lungs. It takes in oxygen from the air you breathe to keep your body working properly by bringing oxygen into your body.
This biological system releases carbon dioxide from the lungs to help you exhale and breathe out properly when you do not have enough oxygen.
The part that brings in the air is called the nose, while the part that releases carbon dioxide and moisture is called the lungs. The nose and lungs are both connected to your throat.
The respiratory system is important for regulating the temperature of the air that goes into the body, and the nose helps you smell.
Circulatory System
The circulatory system consists of the heart and blood vessels. It regulates your body temperature by taking warm blood to the skin’s surface so that heat can escape.
The circulatory system regulates the following functions:
- Heart rate, blood pressure, and volume of blood pumped out to carry oxygen throughout the body
- Circulation of red blood cells in the vessels, which are responsible for carrying oxygen to all parts of the body and returning carbon dioxide to the lungs
- The lymphatic system is responsible for filtering out waste products from your blood. The circulatory system also transports nutrients and oxygen to your cells.
Digestive System
The digestive system consists of the mouth and stomach.
This biological system breaks down food to digest proteins, starches, fats, and carbohydrates. It produces saliva and stomach acids to digest the food. The digestive system also produces enzymes that break down proteins, starches, fats, and carbohydrates in your body.
This system is composed of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. It regulates the following functions:
- Breakdown of food to produce energy and vitamins. The stomach is a major component here, as it produces hydrochloric acid and enzymes to break down proteins, starches, fats, carbohydrates
- Elimination of waste products from the body.
- The small intestine is a major component here, as it absorbs nutrients from the food that has been broken down
- Regulation of blood sugar and body temperature. The liver is a major component here, as it regulates blood sugar levels and releases glucose to the system when needed
The mouth is where the digestive process begins. It chews the food and mixes it with saliva to help break down proteins, starches, fats, carbohydrate
The esophagus is a tube that connects your mouth to your stomach. It moves the food from your mouth into the stomach through peristalsis
The small intestine takes in digested nutrients from carbohydrates and proteins. The large intestine is responsible for eliminating waste products from the body. This elimination is done through the process of excretion.
Endocrine System


The endocrine system consists of hormones. This biological system regulates the following functions:
- Production and secretion of the hormone, which is a chemical that is released by a cell or gland to signal other cells
- Regulation of metabolism and bodily functions. Hormones are intimately involved in this process, and the hypothalamus region of your brain regulates it
- Regulation of growth. Hormones are a major player in regulating this process
- Regulation of reproduction and sexual behaviour. Hormones are also intricately tied into this process
The endocrine system also consists of endocrine glands like pituitary glands, hypothalamus, thyroid glands, and adrenal glands.
Pituitary glands
The pituitary gland is located on the underside of your brain. It releases hormones like growth hormone, prolactin, and thyroid-stimulating hormone. These hormones are important for regulating the body’s growth, and milk production in females and regulating other bodily functions.
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus connects the endocrine and the nervous systems through the pituitary gland. This process happens through signals. The hypothalamus transmits signals from the brain to the respective parts of the body.
Thyroid glands
The thyroid glands are located in your neck, and they produce hormones that regulate metabolism. This metabolism regulation is done by affecting the rate of chemical reactions to make more or less heat.
The thyroid also regulates the following functions:
- Production of energy from broken-down food in your cells
- Aiding the liver in the production of cholesterol
- Regulating how quickly your heart beats and blood circulates through your body
- The thyroid also regulates fertility because it affects the level of hormones in your body.
Muscular System
The muscular system is composed of muscles and joints. This biological system maintains your posture, breathing, and chewing for you to focus on other things.
This biological system consists of muscles and joints that are all connected in various ways. It is responsible for:
- Maintaining your posture
- Providing you with the ability to breathe
- Keeping your chewed food in your mouth and preventing it from going back down into your throat. This is done through the process of mastication.
- Regulating and maintaining your body temperature by shivering and sweating when necessary
- Ensuring that you can move freely throughout your life. The movement is accomplished by contracting muscles to provide movement for joints. The joints are connected to bones in various ways
- Maintaining equilibrium or balance through the process of proprioception
Skeletal System
The skeletal system consists of bones, joints, and cartilage. This biological system protects your internal organs and provides a framework for your body to move about. The roles of the system components are as follows:
- Bones are rigid structures that protect and support your internal organs. There are more than a hundred bones in your body
- Joints are cushions between the bones that allow for movement of those bones. You have more than thirty joints in each appendage
- Cartilage is the slippery material that lines your joints and allows for smooth movement. Cartilages also provide flexibility in your skeletal system
This biological system also includes your skull, which is made up of more than twenty bones. These bones protect the brain and provide a framework for your facial features
Integumentary System


The integumentary system is composed of skin, hair, and nails. This biological system protects the body from damage by outside agents like bacteria or the sun.
The integumentary system is made up of three layers: the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis. These layers are all important for protecting your body from outside agents.
- The epidermis is the outermost layer of skin that protects you against bacteria and other outside agents. It is also responsible for regulating your body temperature
- The dermis layer contains connective tissues that provide support and insulation to the skin layers and contain nerves. The hypodermis is the deepest layer of skin and stores fat
- The integumentary system also includes hair, which is a filamentous outgrowth that is secreted by the epidermis. Hair provides insulation and protection for your head
- Nails are made up of a hard protein called keratin. They protect the ends of your fingers and toes from damage
You may be interested in Common Macromolecule Structure
Final Thoughts
The human body is a complex system with many biological systems that work together to keep us alive and healthy. These include the respiratory, digestive, nervous, endocrine, circulatory, lymphatic, and immune systems. This post looked at some of these important systems in more detail so you can better understand how they affect your health.
Research further to understand more about the biological systems and the many functions that keep your body going. Our premium writers are also ready to help in case you get stuck. All you have to do is place an order today!